Mastering Letter of Credit (LC) and UCP 600: A Complete Guide for Trade Professionals

In today’s complex world of international trade, ensuring secure and reliable payment methods is not just important—it’s essential. Letters of Credit (LC) serve as one of the most trusted financial instruments, providing assurance to both exporters and importers. Backed by UCP 600 (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits), LCs function under globally accepted rules established by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). Whether you’re a trade finance professional, an exporter/importer, a banker, or a student preparing for global trade certifications, mastering the concepts of LC and UCP 600 is crucial to ensuring smooth cross-border transactions. What is a Letter of Credit? A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial document issued by a bank, guaranteeing that a seller will receive payment from the buyer, provided the terms and conditions specified in the LC are fulfilled and documented. Key Players in an LC Transaction: What is UCP 600? UCP 600 (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits) is a set of standardized rules published by the ICC (Publication No. 600). It governs the use of letters of credit worldwide. Key Features of UCP 600: Why Understanding LC and UCP 600 is Critical ✅ Minimize Payment Risk: Ensures seller receives payment if compliant documents are submitted✅ Build Trust in Trade Relationships: Backed by global legal standards✅ Avoid Discrepancies and Rejections: Knowing UCP 600 rules helps avoid common document errors✅ Gain Competitive Edge: Professionals with in-depth LC knowledge are highly valued in banking, logistics, and export-import roles Master the LC Process Step-by-Step Each stage involves crucial documentation and compliance—get one step wrong, and you risk delayed payments or rejection. Common Types of LCs Explained Common Mistakes to Avoid 🚫 Misspelling names or addresses🚫 Presenting documents late🚫 Inconsistencies between invoice and LC terms🚫 Submitting expired documents Learn from Experts: Enroll in Our Practical Course on LC & UCP 600 If you’re looking to master Letters of Credit and UCP 600 from scratch to expert level, we’ve created a comprehensive, easy-to-follow course with real-world case studies, document templates, and exam-focused insights. 👉 Enroll in the Full Course Here – Mastering Letter of Credit (LC) & UCP 600 Whether you’re preparing for a trade finance job, upgrading your skills, or dealing with LCs regularly, this course is tailored for you! What You’ll Learn in the Course: ✅ Complete overview of LC process✅ Deep dive into UCP 600 Articles with practical examples✅ Common discrepancies and how to avoid them✅ Hands-on documentation workshop✅ Real case studies from global trade transactions✅ Quiz-based learning and final certification Who Should Take This Course? Understanding and mastering Letters of Credit and UCP 600 is not just about rules and paperwork—it’s about safeguarding your payments, building credibility, and enabling smooth international trade. Equip yourself with the right knowledge and tools to handle LCs with confidence. 👉 Click here to start learning with our expert-designed course now
English Grammar Guide from A1 to C2 (CEFR Levels)

Understanding grammar is key to mastering any language — and English is no exception. Whether you’re just starting out or refining your advanced fluency, this guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of English grammar across CEFR levels (A1–C2). Let’s explore what grammar topics you should focus on at each stage of your learning journey. 📘 What is CEFR? The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) is a globally recognized standard that describes language ability on a scale from A1 (beginner) to C2 (mastery). It’s used by teachers, learners, employers, and exam boards to measure language proficiency. A1 Grammar (Beginner) At this level, learners can form simple sentences and express basic needs and personal information. Key Grammar Topics: A2 Grammar (Elementary) At this stage, learners begin to describe events, talk about routines, and ask for information. Key Grammar Topics: B1 Grammar (Intermediate) Learners at this level can express opinions, describe future plans, and talk about past experiences. Key Grammar Topics: B2 Grammar (Upper-Intermediate) Learners become more fluent and flexible in their speech and writing with a growing command over complex grammar. Key Grammar Topics: C1 Grammar (Advanced) Learners can use grammar with accuracy, even in academic or professional settings. Tone and register become more important. Key Grammar Topics: C2 Grammar (Proficiency) At this mastery level, grammar use is natural, precise, and sophisticated, even in nuanced discussions and academic writing. Key Grammar Topics: 🎯 Practice Makes Perfect! 📝 Ready to test your grammar knowledge?👉 Take our FREE English Grammar Practice Test here 📝 Final Words Grammar learning is a layered journey. Start with simple sentence patterns at A1 and work your way up to mastering the art of nuanced expression at C2. Bookmark this guide and come back whenever you need a quick grammar refresh at your level.
MongoDB – C100DBA Certified Database Administrator Associate: A Comprehensive GuideMongoDB C100DBA Certified Database Administrator Associate: Career Insights and Salary Trends

In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, the demand for skilled database administrators is on the rise, particularly for NoSQL databases like MongoDB. With its high scalability, flexibility, and ability to handle large volumes of data, MongoDB is widely adopted across industries, from e-commerce to healthcare. For those looking to validate their expertise and secure a competitive edge in this field, the MongoDB C100DBA Certified Database Administrator Associate certification is an excellent pathway. In this blog, we’ll explore the MongoDB C100DBA certification, its significance, how to prepare for it, and discuss salary and job market trends that highlight the growing demand for MongoDB-certified professionals. What is the MongoDB C100DBA Certification? The C100DBA Certified Database Administrator Associate certification is designed to validate a professional’s ability to manage, maintain, and administer MongoDB databases. As one of the most recognized certifications in the NoSQL space, it equips database administrators with the skills required to perform essential DBA tasks, including database design, monitoring, security, backup, and performance optimization. Earning the C100DBA certification demonstrates your ability to handle complex MongoDB database systems, ensuring you stand out in the job market as a skilled MongoDB administrator. Why Pursue the C100DBA Certification? Key Skills Tested in the C100DBA Exam The MongoDB C100DBA certification exam assesses your knowledge and practical skills across various topics essential for database administrators working with MongoDB. The core areas include: How to Prepare for the C100DBA Exam Preparation for the C100DBA exam involves both theoretical learning and practical experience. Here are some strategies to guide your preparation: Salary Insights and Job Market Trends for MongoDB DBAs Salary Overview The salary for MongoDB Certified Database Administrators can vary based on factors such as experience, location, and industry. Here’s an overview of the typical salary ranges for MongoDB DBAs: Factors Affecting MongoDB DBA Salaries: Job Market Outlook The demand for MongoDB DBAs is robust, with many industries embracing MongoDB as their go-to database solution for scalable applications. Key industries driving this demand include: Remote Work Opportunities: The rise of remote work has expanded job opportunities for MongoDB DBAs, allowing companies to hire top talent from anywhere in the world. Conclusion The MongoDB C100DBA certification is an invaluable credential for those looking to establish or advance their careers as MongoDB database administrators. Not only does it enhance your technical skills, but it also improves your marketability in an ever-growing job market. With competitive salaries, diverse career opportunities, and an increasing demand for MongoDB expertise across industries, pursuing this certification is a strategic investment in your professional future.
Mastering AZ-140: Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop Specialty – A Comprehensive Guide

In the evolving world of cloud computing and hybrid work environments, Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) has emerged as a powerful solution for secure, scalable, and remote desktop access. If you’re an IT professional aiming to validate your expertise in deploying, managing, and securing virtual desktop infrastructures on Azure, the Microsoft Certified: Azure Virtual Desktop Specialty (Exam AZ-140) is your ideal certification. This blog delves into what AZ-140 entails, why it matters, who should pursue it, and how you can effectively prepare for and pass the exam. What Is AZ-140? AZ-140 is a role-based certification exam designed by Microsoft for IT professionals who want to demonstrate their expertise in planning, delivering, and managing virtual desktop experiences and remote apps on Microsoft Azure. Certification Title: Microsoft Certified: Azure Virtual Desktop SpecialtyExam Code: AZ-140Level: Specialty (Advanced) Who Should Take AZ-140? This certification is tailored for: Prerequisite (Recommended): Candidates should have experience with Azure administration (AZ-104), though it’s not mandatory. Skills Measured in AZ-140 The AZ-140 exam focuses on six core domains: Preparation Tips for AZ-140 1. Microsoft Learn Start with Microsoft’s official learning paths tailored to AZ-140. These include free, interactive modules. 2. Hands-On Labs Practice on Azure by setting up: 3. Online Courses Platforms like Udemy, Pluralsight, or LinkedIn Learning offer structured AZ-140 courses with practical demos. 4. Practice Tests Attempt full-length mock exams to evaluate your readiness and identify weak areas. For Practice Click Here 5. Documentation Review Microsoft’s official documentation on AVD components, FSLogix, and best practices. Real-World Benefits of AZ-140 ✅ Career Growth: Gain recognition as a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) expert✅ High Demand: AVD is essential in remote and hybrid workplaces✅ Cloud Proficiency: Boosts your credibility in cloud computing and Azure ecosystems✅ Future-Ready Skills: Aligns with the industry’s shift toward cloud-based desktop delivery Exam Details at a Glance Detail Information Exam Code AZ-140 Exam Duration 120 minutes Number of Questions 40–60 (varies) Passing Score 700 / 1000 Cost USD $165 (may vary by location) Format Multiple-choice, case studies Language English, Japanese, Chinese, etc. Final Thoughts The AZ-140 certification is a strategic move for professionals who manage and optimize Azure-based virtual desktops. With remote work now the norm and secure application delivery more important than ever, mastering Azure Virtual Desktop technologies sets you apart in the job market. Whether you’re an IT admin looking to upskill or a consultant designing enterprise solutions, AZ-140 validates your ability to build scalable, secure, and user-friendly desktop experiences in the cloud. Resources to Get Started
MB-300: Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Core Finance and Operations – Your Gateway to ERP Mastery

In the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP), Microsoft Dynamics 365 stands tall as a powerful suite that combines CRM and ERP capabilities. If you’re a finance, operations, or IT professional looking to master the core capabilities of Dynamics 365, the MB-300 certification is your essential starting point. In this blog, we’ll break down what MB-300 is, who it’s for, what you’ll learn, and how to prepare effectively for success. What Is MB-300? MB-300: Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Core Finance and Operations is a certification exam designed by Microsoft to validate your foundational knowledge of the core functionalities within Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations apps. It is a prerequisite exam for various role-based certifications such as: Who Should Take MB-300? This certification is ideal for: Key Skills Measured The MB-300 exam focuses on five core areas: 1. Use Common Functionality and Implementation Tools (20–25%) 2. Configure Security, Processes, and Options (30–35%) 3. Perform Data Migration (10–15%) 4. Validate and Support the Solution (20–25%) 5. Manage Finance and Operations Apps (10–15%) Exam Details Feature Details Exam Code MB-300 Duration ~150 minutes Questions 40–60 (scenario-based, MCQs, drag-and-drop) Passing Score 700 / 1000 Cost $165 USD (may vary by location) Prerequisites None officially, but functional knowledge helps Languages Available English, Japanese, German, French, and more 📚 How to Prepare for MB-300 1. Understand the Exam Guide Download the official exam skills outline from Microsoft Learn. It offers a clear roadmap of what’s tested. 2. Use Microsoft Learn Modules (FREE) Microsoft offers free, in-depth learning paths: 3. Hands-On Practice Use Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations trial environments to practice: 4. Enroll in Instructor-Led or Online Courses Platforms like: offer detailed courses with labs and simulations. 🔹 5. Attempt Practice Tests Use simulated exams to gauge your knowledge. Look for updated 2024-aligned MB-300 mock exams. Latest MB 300 Practice Test Career Benefits of MB-300 Certification ✅ Recognition as a certified Dynamics 365 professional✅ Opens doors to roles like ERP Functional Consultant, Business Analyst, Systems Administrator✅ Higher chances of promotion and better salary prospects✅ Ideal foundation to pursue MB-310 (Finance) or MB-330 (Supply Chain) certifications✅ Valuable for businesses moving to Microsoft cloud-based ERP The MB-300 is not just a certification—it’s a gateway into the heart of Microsoft’s enterprise ERP ecosystem. Whether you’re transitioning into the world of Microsoft Dynamics 365 or enhancing your professional ERP toolkit, this exam will empower you to configure, manage, and support robust, real-world business solutions. Start small, practice consistently, and stay hands-on. Your journey to becoming a certified Microsoft Dynamics 365 expert starts here. Latest MB 300 Practice Test
A New Age of Mutual Fund Flexibility: Introducing Cash Withdrawals Without Redeeming Units
In the modern age, mutual funds have gained popularity as one of the most accessible and diversified forms of investment. Individuals invest in mutual funds to generate wealth over the long term, take advantage of professional fund management, and achieve goals ranging from buying a home to securing their child’s education. Despite their advantages, mutual funds traditionally suffer from one drawback: liquidity. Most mutual fund investors cannot access cash immediately without selling or redeeming their units. The process of redeeming units for cash can take a few days and may involve tax implications or penalties, depending on the type of fund and the holding period. But what if mutual funds could offer a new kind of flexibility—cash withdrawals without redeeming units, much like withdrawing from a savings account? Imagine being able to withdraw a percentage of your mutual fund investment from an ATM without selling your units. You could tap into your investment without liquidating it, allowing it to continue growing while you manage short-term needs. Such an innovation could revolutionize the mutual fund industry by making it more liquid and accessible, and with modern technology, it’s entirely feasible. How Would It Work? The idea is simple yet powerful: mutual fund companies could issue an ATM-like card to investors that would allow them to withdraw a certain percentage of their investment without selling any mutual fund units. The withdrawal limit could be capped at, say, 10% or 20% of the total investment amount, depending on factors like the fund’s liquidity, investor profile, and the type of investment. These withdrawals could be processed in real time, with funds credited to the investor’s bank account or made available as cash at ATMs. The units corresponding to the withdrawal would not be redeemed, meaning the investor’s ownership in the mutual fund would remain intact. Essentially, it would act like a loan against one’s own investment, enabling quick access to cash while still benefiting from the long-term returns of mutual funds. Two-Factor Authentication for Security Given the rise of cybercrime and financial fraud, security is paramount in any new financial feature. Mutual fund companies can ensure secure transactions by incorporating two-factor authentication (2FA) into the withdrawal process. When an investor initiates a withdrawal, a unique code could be sent to their registered mobile number or email address, much like how banks operate for online transactions today. This extra layer of security will ensure that unauthorized individuals cannot withdraw funds, protecting investors from fraud and identity theft. Furthermore, companies could introduce additional security measures, such as biometric verification or a PIN, to add another layer of protection. This would make the process both convenient and secure, giving investors peace of mind while accessing their funds. Benefits of Cash Withdrawals Without Redeeming Units 1. Increased Liquidity One of the biggest advantages of this system is enhanced liquidity. Mutual fund investments are often seen as medium- to long-term financial commitments. However, life is unpredictable, and there may be situations where an investor needs access to cash immediately. By offering partial cash withdrawals without unit redemption, mutual funds become much more liquid, making them a more attractive option for individuals who may otherwise hesitate to lock up their money in such investments. 2. Reduced Market Timing Risks When investors redeem their mutual fund units, they may face market timing risks. If the market is down, selling units could result in losses or missed growth opportunities. With this new cash withdrawal feature, investors can avoid the need to sell during unfavorable market conditions, keeping their investments intact while still addressing short-term cash needs. 3. Lower Tax Implications In most countries, selling mutual fund units triggers a capital gains tax event, especially for equity-based funds. If investors could withdraw cash without redeeming units, they would potentially avoid such tax implications, as the units would remain in the fund, continuing to grow in value. Tax would only apply when the units are ultimately sold, allowing for more efficient tax planning. 4. Promoting Long-Term Investing One of the common issues mutual fund companies face is that investors often exit prematurely, missing out on potential long-term gains. The ability to withdraw cash without redeeming units can encourage investors to stay invested longer, as they no longer need to liquidate their holdings to access funds. This would foster a long-term investment mindset, which is beneficial for both the investors and the fund itself. 5. Cybercrime Reduction With the addition of secure, two-factor authentication, the risks of cybercrime associated with online transactions could be significantly reduced. The ATM-like card would provide a more secure way of accessing funds than traditional online systems, which are more prone to phishing attacks, malware, and other forms of hacking. This feature, combined with 2FA, will make mutual fund withdrawals a safer process overall. Challenges to Consider Of course, such a system would come with challenges that mutual fund companies and regulators need to address. The primary challenge is liquidity management—mutual fund companies would need to ensure they have enough liquid assets to handle these withdrawals, particularly during periods of market stress. There may also be legal or regulatory hurdles, as many countries have strict rules governing mutual fund redemptions and withdrawals. However, with the right balance of regulation, investor education, and technological innovation, these challenges can be mitigated. Conclusion Allowing cash withdrawals from mutual funds without redeeming units is an idea whose time has come. By offering greater liquidity, reducing tax implications, and providing enhanced security through two-factor authentication, mutual fund companies can create a more flexible, investor-friendly product. This would not only make mutual funds more appealing to a broader audience but also encourage long-term investing habits. The added security features would ensure that this innovative feature does not compromise the safety of investors’ assets, helping to reduce the risk of cybercrime in the process. Ultimately, such a system could mark a significant shift in the way people view mutual funds—not just as long-term investments, but as versatile financial tools that offer both growth and liquidity. This would empower more people to
How to Achieve ₹1 Crore with Mutual Fund Investments: A Simple Guide
Introduction Investing in mutual funds can help you grow your wealth steadily over time. If you have a target amount of ₹1,00,00,000 (1 crore), systematic investment plans (SIPs) are an excellent way to achieve that goal. This blog will guide you on how much you need to invest monthly and how long it will take, based on an expected rate of return from mutual funds. Understanding SIP and Target Goals SIP allows you to invest a fixed amount regularly in mutual funds, which helps in disciplined saving. To achieve a large financial goal like ₹1 crore, it’s important to choose the right SIP amount and have realistic expectations for returns. The rate of return varies based on market conditions, but we will use an assumed rate to estimate the time required. Key Factors: SIP Amount and Rate of Interest Your target can be achieved by balancing two main factors: Calculate Your Investment Journey To make this calculation simple, let’s use an interactive calculator below. You can input your desired SIP amount and expected rate of return to see how many years it will take to accumulate ₹1 crore. Conclusion By using this calculator, you can plan your investments better and stay on track toward achieving ₹1 crore. Remember, starting early and staying consistent in your investment will help you reach your financial goals faster. Refer Below Calculator Rs. 1 Crore SIP Goal Calculator Rs. 1 Crore – Goal Monthly SIP Amount (Rs.): Expected Annual Return Rate (%): Calculate Time
Why Renting Can Be a Smart Financial Choice Over Buying a Home in the USA

The American Dream has long included owning a home as a cornerstone. For many, the idea of having a place to call their own, with a white picket fence and the promise of equity, has made homeownership seem like the ultimate goal. However, in recent years, the financial landscape has shifted, and many are finding that renting can be a more practical and financially sound choice over owning a home. Here’s why, in today’s economic environment, staying in a rented house may be a wiser decision than purchasing one. 1. Upfront Costs and Flexibility Owning a home involves a significant financial commitment. The down payment, typically 20% of the home’s value, closing costs, moving expenses, and other fees can add up to tens of thousands of dollars. In contrast, renting requires far less upfront capital—usually just a security deposit, the first month’s rent, and sometimes a small application fee. For those who may not have substantial savings or who want to keep their money liquid, renting allows for greater flexibility. The ability to move for a new job, live in different areas, or adjust to changing family situations without worrying about the lengthy process of selling a home can be a huge advantage. Especially in uncertain times, the financial flexibility renting offers is invaluable. 2. Maintenance and Repairs Homeownership comes with ongoing responsibilities, not the least of which are maintenance and repairs. From leaky roofs to broken appliances, homeowners are on the hook for the cost of fixing anything that goes wrong. These unexpected expenses can quickly add up and blow through any household budget. In contrast, when renting, the landlord is responsible for maintenance. Tenants can rest easy knowing they won’t have to pay out of pocket for emergency repairs or the general upkeep of the property. This lack of responsibility for repairs and maintenance frees up both time and money, making renting especially appealing to those who prefer to focus on other financial goals or simply avoid the hassles of homeownership. 3. Property Taxes and Insurance Homeowners are required to pay property taxes, which can vary widely depending on the location. Property taxes often increase over time, adding to the total cost of owning a home. For many, these annual taxes can come as a surprise, as they can run into thousands of dollars per year. On top of that, homeowners’ insurance is another required expense that adds to the cost of ownership. Renters, on the other hand, are not responsible for property taxes, and renters’ insurance is typically much cheaper than homeowners’ insurance. While renters’ insurance is highly recommended, it is not always mandatory and usually covers just personal belongings, which makes it a smaller financial burden than homeowners’ insurance. 4. Opportunity Cost and Investments One of the most significant reasons renting might be more financially advantageous than owning is the opportunity cost. The money you save by not making a large down payment or handling property-related costs could be invested in other areas, like stocks, bonds, or retirement accounts, which may yield higher returns than the appreciation of a home’s value. Over time, the stock market has historically outperformed real estate, making it a potentially more lucrative way to build wealth. If you’re renting, you have the freedom to invest in higher-yield opportunities rather than being tied to a single asset that can fluctuate with the housing market. Additionally, diversifying investments can provide a more secure financial foundation. 5. Housing Market Volatility The real estate market can be unpredictable. While housing prices generally rise over time, there are periods when they fall dramatically, such as during the 2008 financial crisis. Homeowners who bought at the peak of the market found themselves underwater on their mortgages—owing more than their homes were worth. This kind of risk can be daunting for many, especially those who may not have the financial security to weather downturns in the housing market. Renting eliminates this risk entirely. You’re not tied to the value of the property, and if the housing market declines, your finances remain unaffected. Renters can simply choose to relocate if prices rise or fall, providing flexibility in uncertain economic times. 6. Mobility and Lifestyle Preferences For those who value mobility, renting offers a level of freedom that homeownership doesn’t. Whether you want to move to a different city for career opportunities, live closer to family, or just try out different neighborhoods, renting gives you the flexibility to make those decisions without the hassle of selling a home. This mobility is particularly valuable in today’s job market, where remote work and frequent career changes are becoming more common. For professionals who don’t want to be tied down to one location, renting provides a sense of freedom that owning a home cannot match. 7. Unpredictable Homeownership Costs While a mortgage payment may seem like a fixed cost, homeownership is full of unpredictable expenses that can be difficult to budget for. Property taxes can increase, utility bills may fluctuate, and repairs or renovations are often needed. These expenses can add up quickly, turning what seemed like a manageable monthly payment into a financial strain. Renting, on the other hand, typically involves predictable monthly payments. Some rental agreements even include utilities, making it easier to plan and budget. Renters aren’t caught off guard by unexpected expenses, giving them more control over their financial situation. Savings Example: Renting vs. Buying Let’s take a closer look at an example of how renting can result in significant savings compared to homeownership: Imagine you’re deciding between buying a $400,000 home or renting a comparable property for $2,500 per month. Here’s a breakdown of the potential costs for both scenarios over five years: Homeownership Costs: Total Monthly Costs for Homeownership: Total Monthly Cost: $2,794 In addition to the monthly expenses, you would have also paid $80,000 upfront for the down payment. Renting Costs: Now, let’s consider renting a similar property for $2,500 per month. Renters don’t have to worry about property taxes, maintenance, or hefty insurance premiums. Renters’ insurance, which covers personal belongings, is typically
Mastering the 50:30:20 Rule: A Simple Formula for Financial Success
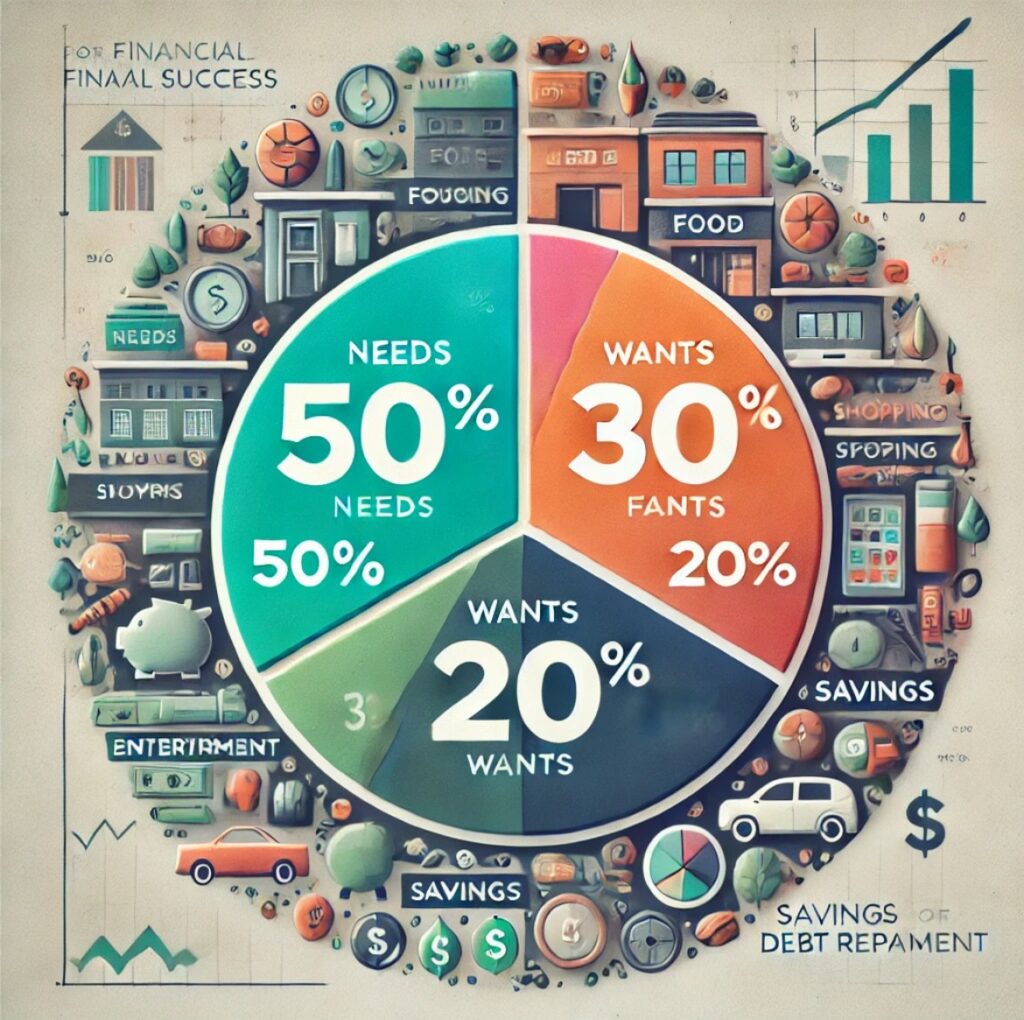
In a world where managing finances can feel overwhelming, the 50:30:20 rule offers a simple, effective framework to help individuals achieve financial stability and long-term goals. This budgeting strategy divides income into three broad categories—needs, wants, and savings—giving people a clear roadmap to manage their money in a balanced and sustainable way. Whether you are just starting your financial journey or looking to regain control over your finances, understanding and applying the 50:30:20 rule can set you on the path to success. What is the 50:30:20 Rule? The 50:30:20 rule is a straightforward budgeting guideline that helps you allocate your income into three essential areas: Why the 50:30:20 Rule Works The beauty of the 50:30:20 rule lies in its simplicity. Instead of getting bogged down by complicated budgets or detailed expense tracking, this rule provides a clear structure that is easy to implement and maintain. It is flexible enough to adapt to most financial situations, while also ensuring that you are living within your means, enjoying life, and preparing for the future. Here’s why the 50:30:20 rule is so effective: How to Implement the 50:30:20 Rule If you’re ready to implement the 50:30:20 rule, follow these simple steps: Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them While the 50:30:20 rule is straightforward, some people may face challenges when trying to implement it. Here are a few common obstacles and tips for overcoming them: Conclusion The 50:30:20 rule is a simple yet powerful tool for managing your finances. By dividing your income into three main categories—needs, wants, and savings—it offers a balanced approach to budgeting that helps you cover essential expenses, enjoy life, and build a secure financial future. Whether you’re just starting to budget or looking for a fresh approach to managing your money, the 50:30:20 rule can provide the structure you need to achieve financial success.
Understanding Employment Taxes in the USA: A Comprehensive Guide with Practical Examples

Introduction Navigating employment taxes in the United States can be complex, especially for those who are new to the workforce, self-employed, or small business owners. Employment taxes are an essential component of the country’s taxation system, contributing to vital services such as Social Security and Medicare. Understanding how these taxes work, the rates applied, and how to calculate them is critical for both employees and employers. In this blog, we will explore the fundamentals of employment taxes, break down the components, and provide practical examples to clarify common scenarios. What Are Employment Taxes? Employment taxes in the U.S. are the taxes that both employers and employees must pay to fund Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance programs. These taxes ensure that the government has sufficient revenue to provide benefits to retirees, the disabled, and other eligible individuals. Employment taxes can be broken down into several main categories: Each of these taxes has different rates and requirements, and we will explore them individually with examples. 1. Federal Income Tax Withholding Federal income tax is deducted from an employee’s paycheck by the employer based on the employee’s earnings and filing status (single, married, etc.). Employers use the information provided by employees on Form W-4 to determine the correct amount to withhold. The federal income tax is progressive, meaning the more you earn, the higher your tax rate. Example: Let’s say Sarah, a single individual, earns $50,000 a year. Based on her W-4 and the IRS tax tables, her employer calculates that $6,000 should be withheld from her paycheck throughout the year for federal income taxes. This is deducted gradually with each paycheck. 2. Social Security Tax (FICA) The Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) mandates that Social Security taxes are withheld from employees’ wages. For 2023, the Social Security tax rate is 6.2% for employees, with a wage base limit of $160,200. This means that only the first $160,200 of an employee’s earnings are subject to the Social Security tax. Employers are required to match the 6.2% contribution, meaning they also contribute 6.2% of each employee’s wages to Social Security. Example: If John earns $70,000 in 2023, his Social Security tax will be 6.2% of his earnings, which amounts to $4,340. His employer will also contribute the same amount, for a total of $8,680 being paid into Social Security on behalf of John. 3. Medicare Tax (FICA) Medicare tax, also under FICA, funds the health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older and for certain younger individuals with disabilities. The Medicare tax rate is 1.45% of an employee’s wages, and unlike Social Security tax, there is no wage base limit. Employers are required to match this contribution. An additional 0.9% Medicare tax is levied on employees earning more than $200,000 a year. Employers are not required to match the additional Medicare tax. Example: Lisa earns $150,000 per year. Her Medicare tax will be 1.45% of $150,000, which equals $2,175. Her employer will also contribute the same amount. Since Lisa’s income is below the $200,000 threshold, the additional 0.9% tax does not apply to her. However, if Lisa earns $250,000, she would owe an extra 0.9% Medicare tax on the $50,000 she earns over the $200,000 threshold. In this case, she would owe an additional $450 in Medicare taxes. 4. Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA) FUTA taxes fund unemployment benefits for workers who lose their jobs. Unlike the other taxes mentioned, employees do not pay FUTA tax; only employers are responsible for paying it. The FUTA tax rate is 6.0% on the first $7,000 of an employee’s wages. However, employers may receive a credit of up to 5.4% for paying state unemployment taxes, which reduces the effective FUTA tax rate to 0.6%. Example: If Mark’s employer pays him $10,000 in wages, only the first $7,000 is subject to FUTA. Assuming the employer qualifies for the full 5.4% credit, the employer would pay 0.6% of $7,000, which equals $42 in FUTA taxes for Mark. 5. State Income Taxes Many states also impose their own income taxes, which are deducted from employees’ paychecks in addition to federal taxes. Each state sets its own tax rates, brackets, and rules for deductions. Some states, such as Florida, Texas, and Washington, have no state income tax. Example: Jane lives and works in California, which has a progressive state income tax. If she earns $60,000 annually, her state tax liability may range from 1% to 9.3%, depending on her income bracket. California has one of the higher state income tax rates in the country. Employment Taxes for Self-Employed Individuals Self-employed individuals must pay both the employee and employer portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. This is referred to as the Self-Employment Tax, which is 15.3% (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare) on net earnings up to the Social Security wage base limit. Example: Tom, a freelancer, earns $100,000 from his business. He will need to pay 12.4% of his income up to the $160,200 limit in Social Security taxes, plus 2.9% for Medicare. In total, Tom’s self-employment tax will amount to $15,300. Conclusion Understanding employment taxes is crucial for both employees and employers in the U.S. It ensures compliance with federal and state tax regulations, while also contributing to key social programs like Social Security and Medicare. For employees, it’s important to review your paycheck regularly to ensure correct withholding amounts. For employers and self-employed individuals, staying informed about tax obligations can help avoid costly mistakes and ensure smooth operations. By breaking down each tax with practical examples, you can now navigate the intricacies of employment taxes more confidently. Whether you are employed, self-employed, or running a business, understanding these taxes is key to financial planning and long-term success.